
Insulated Glass Options
Discover the potential of insulated glass for energy-efficient building design. Explore options, technologies, and benefits.
Insulated Glass Options: Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Comfort
In today’s ever-evolving world of building design, energy efficiency and sustainability are paramount concerns. Architects, homeowners, and construction professionals are continually seeking the best solutions to optimize energy performance while enhancing comfort levels. Insulated glass, a long-standing technology, offers a promising avenue for achieving these goals. However, the challenge lies in identifying the most suitable insulated glass options for each project and harnessing the latest advancements in the field.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the realm of insulated glass and its wide range of options. We will delve into the intricacies of choosing the right type of insulated glass for specific projects and leveraging cutting-edge technologies to maximize energy efficiency. By understanding the various components and factors that influence the selection process, you can navigate the world of insulated glass with confidence and overcome the associated challenges.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the world of insulated glass, where the focus is not only on its longstanding presence but also on harnessing its full potential. Whether you are an architect, homeowner, or building professional, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights to make informed decisions and propel your projects towards exceptional energy performance and optimal comfort. Let’s uncover the possibilities of insulated glass and discover how it can revolutionise your approach to sustainable building design.
Types of Insulated Glass
Insulated glass is available in various configurations, each offering unique benefits for energy efficiency and comfort. Let’s explore the different types of insulated glass, including the revolutionary Vacuum Glazing technology:
1. Double Glazing
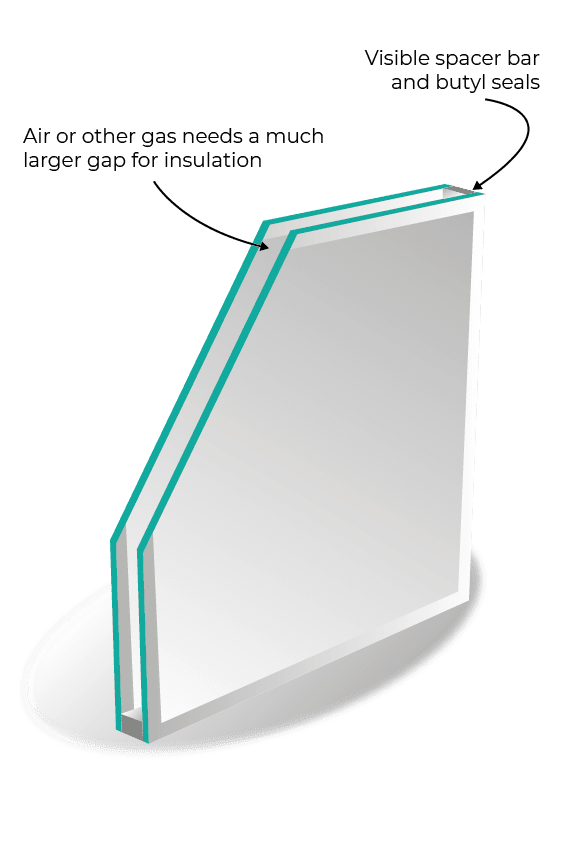
Double glazing is a popular choice for enhancing insulation in windows. It consists of two glass panes separated by a sealed air or gas-filled space. The gap between the panes acts as a barrier, reducing heat transfer and improving thermal efficiency. Argon or krypton gases are commonly used to fill the space between the glass panes in double glazing, further enhancing insulation properties.
2. Triple Glazing
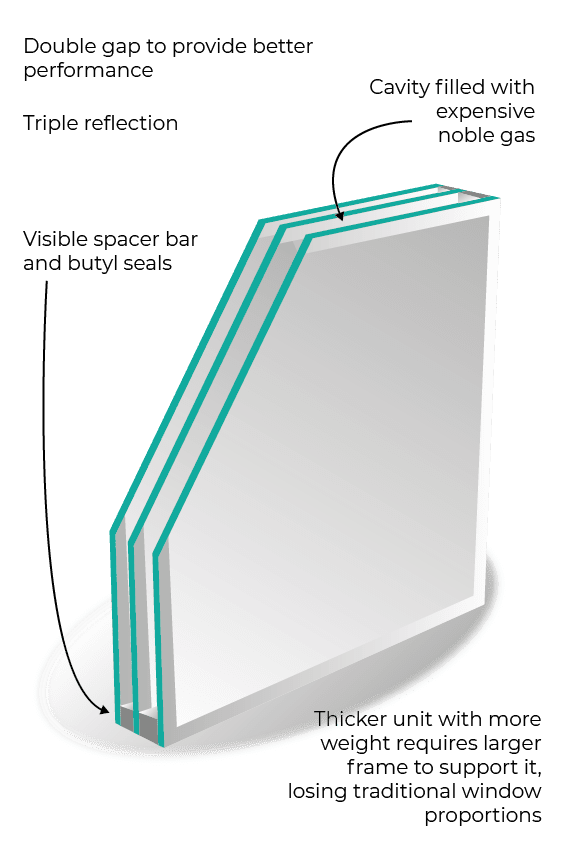
For even higher levels of insulation, triple glazing is an excellent option. Triple glazing incorporates an additional glass pane, creating two sealed air or gas-filled spaces between the panes. The extra layer of glass enhances thermal performance, making it ideal for regions with harsh climates or noise pollution concerns.
3. Vacuum Glazing
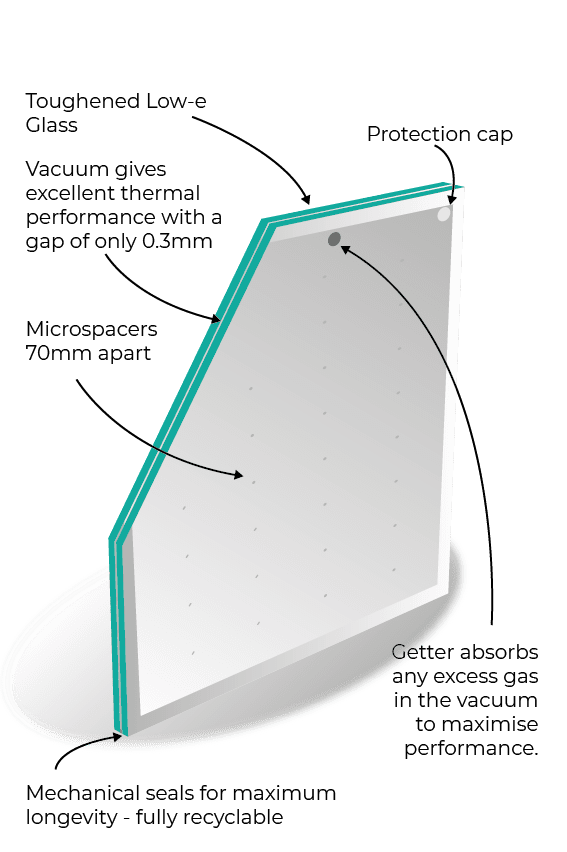
Introducing the cutting-edge technology of Vacuum Glazing. Unlike traditional insulated glass units, Vacuum Glazing utilizes a vacuum-sealed space between the glass panes, eliminating the need for gas filling. The absence of air or gas in the gap virtually eliminates heat transfer, resulting in exceptional thermal insulation. Vacuum Glazing offers a slim profile and superior thermal performance, making it an excellent choice for both residential and commercial applications.
Each type of insulated glass has its own advantages, so it’s essential to consider factors such as climate, budget, and specific project requirements when making a selection. Now that we have explored the types of insulated glass available, let’s move on to the benefits they offer in Section 3.
Components and Construction
Insulated glass is a complex assembly consisting of multiple components carefully designed to maximise energy efficiency and performance. Understanding the various parts of insulated glass is crucial in selecting the right configuration for your needs. Let’s explore the key elements:
1. Glass Types
Different types of glass can be used in insulated glass units, each with its own characteristics and performance attributes. Common options include float glass, tempered glass, laminated glass, and low-iron glass. These glass types can be combined to meet specific requirements for safety, soundproofing, thermal insulation, or solar control.
2. Spacer Systems
The spacer system is a crucial component that separates and seals the glass panes in an insulated glass unit. It helps maintain the cavity width and provides structural integrity. Spacer materials can be made of aluminum, stainless steel, or non-metallic materials like warm-edge spacers, which offer superior thermal performance by reducing heat transfer at the edges of the glass.
3. Cavity Contents
The space between the glass panes, known as the cavity, can be filled with air or gas. Argon, krypton, or a mixture of both gases are commonly used in double and triple glazing units to enhance insulation properties. These gases have higher thermal resistance than air, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. In addition to gas-filled cavities, advancing technologies such as vacuum glass have emerged as an innovative solution. Vacuum glazing utilises a completely sealed vacuum cavity, eliminating the need for gas-filled spaces. This cutting-edge technology offers superior insulation performance, significantly reducing heat loss and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
4. Sealants and Adhesives
To ensure long-term performance and durability, the glass panes and spacer system are sealed together using high-quality sealants and adhesives. The sealants create an airtight and watertight seal, preventing moisture infiltration and maintaining the insulating properties of the unit. The adhesives provide structural support and bond the components securely. However, in ultra-slim double glazing, the narrowness of the gap can pose challenges for sealants and adhesives, increasing the risk of seal failure over time. This limitation is overcome in vacuum glazing, as the use of a flexible edge sealant ensures effective sealing even in narrow gaps, guaranteeing long-lasting performance and superior insulation properties.
5. Coatings and Films
Insulated glass can feature various coatings and films applied to the glass surfaces. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings, for example, help control heat transfer by reflecting infrared radiation while allowing visible light to pass through. Other coatings, such as solar control coatings or self-cleaning coatings, can provide additional benefits such as reducing glare or minimizing maintenance requirements.
By carefully selecting the types of glass, spacer systems, cavity contents, sealants, and coatings, manufacturers create customised insulated glass units tailored to specific requirements. These components work together to enhance thermal efficiency, sound insulation, and overall performance. Now that we understand the construction of insulated glass, let’s move on to the benefits it offers in Section 4.
Benefits of Insulated Glass
Insulated glass offers a range of benefits that make it a popular choice for residential and commercial applications. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
1. Enhanced Energy Efficiency:
One of the primary benefits of insulated glass is its superior thermal insulation properties. The multiple layers of glass, along with the air or gas-filled cavity, act as an effective barrier to heat transfer. This helps to minimise heat loss during colder months and reduce heat gain in warmer seasons, leading to energy savings and improved energy efficiency.
Read more about U-Values on this Wikipedia page: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_transmittance
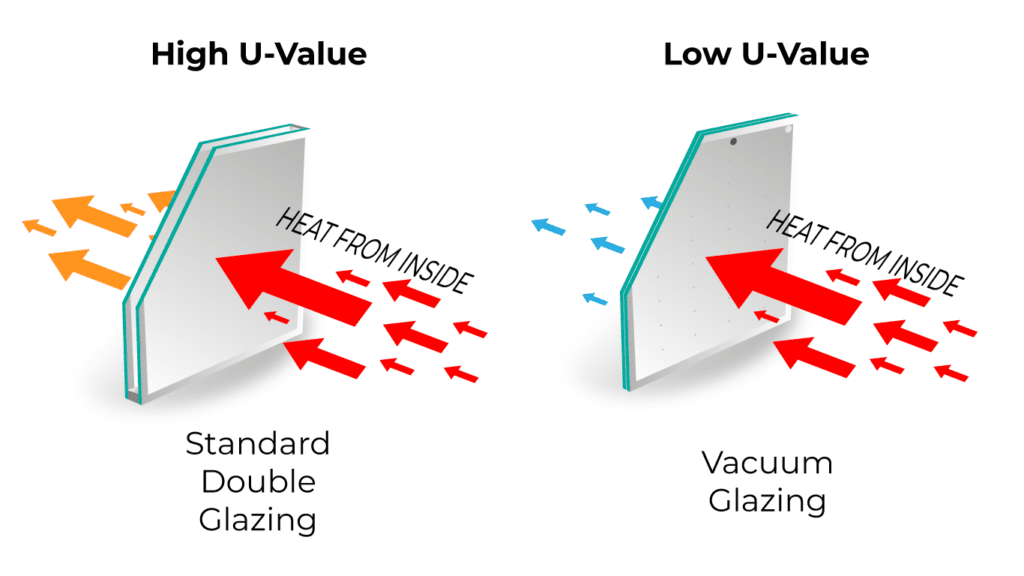
2. Improved Indoor Comfort:
By reducing heat transfer, insulated glass helps to maintain a more consistent indoor temperature. It minimises cold drafts near windows and prevents excessive heat buildup, creating a comfortable living or working environment throughout the year. This not only enhances occupant comfort but also reduces the reliance on heating and cooling systems.
3. Noise Reduction
Insulated glass provides excellent sound insulation, making it an ideal choice for areas exposed to high noise levels, such as busy streets or airports. The combination of multiple glass layers and the insulating airspace helps to dampen external noise, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment.
4. Condensation Control
Insulated glass significantly reduces the likelihood of condensation forming on the interior surface of windows. The thermal barrier created by the insulating airspace helps to maintain a warmer glass temperature, minimising condensation buildup and potential moisture-related issues such as mould and mildew.
5. UV Protection
Insulated glass can be equipped with coatings that help to block a significant amount of harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV rays can cause fading and damage to furnishings, artwork, and flooring over time. With insulated glass with the correct coatings, you can protect your interior spaces and preserve the longevity of valuable assets.
6. Sustainability and Energy Savings
The energy efficiency of insulated glass contributes to sustainability by reducing reliance on artificial heating and cooling. By minimising energy consumption, insulated glass helps to lower greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the environmental impact of buildings. Additionally, reduced energy usage translates into long-term cost savings for homeowners and businesses.
7. Versatility and Design Options
Insulated glass offers a wide range of design possibilities, allowing architects and designers to create visually appealing spaces. It is available in various glass types, thicknesses, coatings, and patterns, enabling customisation to meet specific aesthetic requirements. Insulated glass can seamlessly integrate with different architectural styles while providing the desired performance characteristics. For example, the ultra-low profile of vacuum glazing (8mm) makes it ideal for heritage buildings where planning officers would specify single glazing.
Incorporating insulated glass into your windows and glazing systems can provide numerous advantages, including improved energy efficiency, enhanced comfort, noise reduction, condensation control, UV protection, sustainability, and design versatility. In the next section, we will discuss the longevity and installation considerations of insulated glass, highlighting the importance of professional installation and proper maintenance.
Factors to Consider
When selecting insulated glass for your project, it’s essential to consider various factors to ensure optimal performance and long-term satisfaction. Here are key factors to keep in mind:
1. Energy Efficiency
Look for insulated glass units with low U-values and high R-values, indicating superior thermal insulation. This helps to minimize heat transfer and reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling.
2. Glazing Configuration
Consider the number of glass panes and the thickness of each pane in the insulated glass unit. Multiple layers of glass with a wider cavity between them offer improved thermal insulation and soundproofing properties.
3. Gas Filling
Insulated glass units are often filled with inert gases like argon or krypton to enhance their thermal performance. Check if the selected glass unit includes gas filling and ensure it complies with energy efficiency standards.
4. Coatings and Treatments
Insulated glass can be coated with low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings to reduce heat transfer and enhance energy efficiency. Additionally, consider options like solar control coatings or self-cleaning treatments, depending on your specific requirements.
5. Sound Insulation
If noise reduction is a concern, choose insulated glass units with sound insulation properties. These units are designed to minimize the transmission of external noise, providing a quieter and more comfortable indoor environment.
6. Glass Quality and Durability
Ensure the insulated glass meets industry standards for quality and durability. It should be resistant to impact, thermal stress, and other environmental factors to ensure long-term performance.
7. Installation Expertise
Proper installation is crucial for the optimal performance. Hire experienced professionals who are knowledgeable about handling and installing the units to ensure airtightness, structural integrity, and overall effectiveness.
8. Replacement Considerations
When choosing your glass, it’s important to consider whether you’re replacing the entire window unit or just the glazing. If you’re replacing the entire unit, you’ll need to ensure that the new insulated glass is compatible with the existing frame and hardware. In such cases, opt for units that have the same profile as the existing windows to maintain a consistent appearance. For example, LandVac Optimum triple glazing offers the same profile as double glazing, making it an excellent choice for replacement projects where preserving the original aesthetic is crucial. On the other hand, if you’re only replacing the glazing, make sure to accurately measure the dimensions to ensure a proper fit within the existing frame.
9. Maintenance and Cleaning
Consider the ease of maintenance and cleaning for the selected units. Some coatings or treatments may require specific care instructions, so ensure you understand the recommended cleaning methods and frequency.
10. Warranty and Support
Check the warranty provided by the manufacturer or supplier for the insulated glass units. A reliable warranty ensures protection against manufacturing defects and gives you peace of mind.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right units for your project, maximising energy efficiency, comfort, and longevity. Consulting with industry professionals or glass suppliers can provide valuable guidance and help you make an informed decision.
In the next section, we will delve into the installation and maintenance considerations for insulated glass, highlighting their importance in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the units.
Insulated Glass in Passive House Construction

Insulated glass plays a vital role in Passive House construction, which focuses on creating highly energy-efficient and comfortable buildings. Let’s explore how it contributes to Passive House design principles:
1. Superb Thermal Performance
In Passive House construction, achieving excellent thermal performance is crucial. Insulated glass with low U-values, such as those filled with inert gases like argon or krypton, helps to minimize heat transfer and improve the overall energy efficiency of the building envelope. By using insulated glass in windows and doors, Passive House projects can significantly reduce heating and cooling loads.
2. Airtightness and Reduced Infiltration
To achieve the strict airtightness requirements of Passive House standards, the entire building envelope must be carefully sealed. Insulated glass units are designed and manufactured to ensure airtightness when properly installed. This prevents unwanted air infiltration and heat loss, leading to improved energy performance and increased comfort.
3. Solar Heat Gain and Daylighting
Passive House design emphasizes the effective utilisation of natural resources, including solar heat gain and daylight. Insulated glass units can be customized with selective coatings that allow for optimal solar heat gain during winter months while minimizing excessive heat gain in summer. Additionally, the use of efficient units with high visible light transmission enables ample daylight to penetrate the building, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
4. Thermal Comfort and Condensation Control
Insulated glass helps maintain a comfortable indoor environment in Passive House buildings. With its thermal barrier, it reduces cold spots near windows and minimizes condensation on the interior surface. This ensures a cozy and condensation-free living or working space, promoting occupant well-being and preventing potential moisture-related issues.
5. Sustainability and Reduced Energy Consumption
Passive House construction aligns with sustainable building practices by prioritising energy efficiency and reduced energy consumption. Insulated glass, with its exceptional thermal insulation properties, plays a key role in achieving these objectives. By reducing the reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems, Passive House buildings significantly decrease their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
By incorporating insulated glass into Passive House projects, architects and builders can optimize energy performance, enhance occupant comfort, and create environmentally friendly buildings. The use of high-quality insulated units, coupled with meticulous installation and attention to airtightness, is crucial to achieving the desired energy efficiency and performance levels. In the following section, we will discuss the importance of professional installation and maintenance considerations for insulated glass in more detail.
Planning Regulations and Special Considerations
When choosing windows for your project, it’s crucial to be aware of any planning regulations or special considerations that may affect your decision. Here are a few scenarios where specific factors come into play:
1. Listed Buildings
If your building is listed or located within a conservation area, planning officers may have specific requirements for glazing. In some cases, they may specify single glazing to maintain the historic authenticity of the property. It’s important to consult with the appropriate authorities and understand the regulations before selecting insulated glass.
2. Roof Lights and Tilted Glazing
When considering glazing units located in roof lights or at tilted angles, it’s essential to choose an option that can maintain its insulation properties effectively. Traditional double glazing may lose some of its thermal performance when tilted, making vacuum glazing a preferable choice in such scenarios. Vacuum glazing retains its insulation capabilities even when installed at different angles.
3 Building Regulations
Familiarise yourself with local building regulations and standards that govern glazing installations. These regulations may specify minimum energy efficiency requirements, safety standards, or other criteria that must be met when selecting and installing new windows.
4 Historic Preservation and Design Guidelines
In addition to planning regulations, certain areas or developments may have specific design guidelines or preservation requirements. These guidelines could influence the choice of glazing and may prioritize maintaining the aesthetic appearance or architectural integrity of the building.
When planning your project, engage with relevant authorities, such as planning officers or conservation officers, to understand the specific requirements and limitations related to glazing. Their expertise and guidance can help you navigate any restrictions while ensuring you select an appropriate type of glass that complies with the regulations.
Remember that these considerations may vary depending on your location and the specific regulations in place. Consulting with professionals experienced in working with listed buildings, conservation areas, or specialised glazing installations can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance with all relevant planning regulations.
In the next section, we will discuss the importance of proper installation and maintenance practices for insulated glass, ensuring its longevity and optimal performance over time.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of the units in your building. By following the recommended practices, you can maximize energy efficiency, prevent issues, and extend the service life of your glazing units. Here are some key considerations:
1. Professional Installation
Insulated glass should be installed by experienced professionals who are familiar with the specific product and its installation requirements. Improper installation can compromise the performance of the unit, leading to air or moisture leakage, reduced insulation, or even glass breakage. Hiring a qualified installer ensures that the glass is fitted correctly, with proper sealing and alignment.
2. Sealing and Weatherproofing
Insulated glass units rely on a secure seal to maintain their insulating properties. The perimeter edges of the glass are typically sealed with durable materials like silicone or butyl tape to create an airtight and watertight seal. Adequate weatherproofing measures, such as flashing or weather barriers around the window frame, can further enhance the performance and durability of the installation.
3. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
It’s essential to conduct routine inspections of the windows to identify any signs of damage, degradation, or seal failure. Inspect the seals, frames, and glass for cracks, gaps, or condensation between the panes. Promptly address any issues by contacting a professional glazier to perform necessary repairs or replacements.
4. Cleaning and Care
Maintain the cleanliness of the glass surfaces to ensure unobstructed views and optimal performance. Clean the glass regularly using mild, non-abrasive cleaners and a soft cloth or sponge. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that can damage the glass or coatings. Pay attention to the seals and remove any debris or buildup that may affect their integrity.

5. Seasonal Considerations
Your windows may experience different stress factors during changing seasons. Thermal expansion and contraction can affect the seals, and extreme weather conditions can put additional strain on the unit. Be mindful of seasonal temperature fluctuations and ensure that the installation is designed to accommodate these variations.
By following these installation and maintenance practices, you can optimize the performance and longevity of your units. Regular care and attention will help preserve their energy efficiency, reduce the risk of issues, and ensure a comfortable and sustainable environment within your building.
In the final section of this post, we’ll summarise the key points discussed and conclude with the importance of choosing the right insulated glass solution for your specific needs.
Summary and Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the world of insulated glass and its significance in modern building design. Insulated glass offers a range of benefits, including enhanced energy efficiency, improved comfort, reduced condensation, and noise reduction. By incorporating it into your windows and facades, you can create a more sustainable and comfortable living or working environment.
We discussed the different types of insulated windows, such as double glazing, triple glazing, and vacuum glazing. Each type has its unique characteristics and performance attributes, allowing you to choose the most suitable option based on your specific requirements.
Furthermore, we highlighted the importance of factors such as low-emissivity coatings, gas fillings, and proper sealing in achieving optimal energy performance and thermal insulation. The choice of materials, such as different types of glass and coatings, contributes to the overall performance and appearance of insulated glass units.
We also recognised the role of insulated glass in passive house construction, where its exceptional thermal insulation properties play a vital role in achieving high energy efficiency and sustainability goals.
Moreover, we discussed various factors to consider when selecting insulated glass, including local regulations and planning requirements. Understanding these factors ensures compliance and helps you make informed decisions that align with the unique needs of your project.
Lastly, we emphasised the importance of professional installation and regular maintenance to maximise the longevity and performance of your windows. By following proper installation techniques and implementing routine care practices, you can preserve the energy efficiency and durability of your glazing units.
In conclusion, insulated glass is a valuable solution for improving energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability in modern buildings. It provides numerous benefits and plays a vital role in achieving green building certifications and meeting the evolving demands of energy-conscious architecture.
When considering your options, it is essential to consult with experienced professionals who can guide you through the selection process and ensure a successful installation. By choosing the right solution and adhering to proper maintenance practices, you can enjoy the advantages of energy-efficient glazing for years to come.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of insulated glass and its significance in contemporary building design. Should you have any further questions or require assistance with your project, feel free to reach out to our knowledgeable team.